Robotic Vision
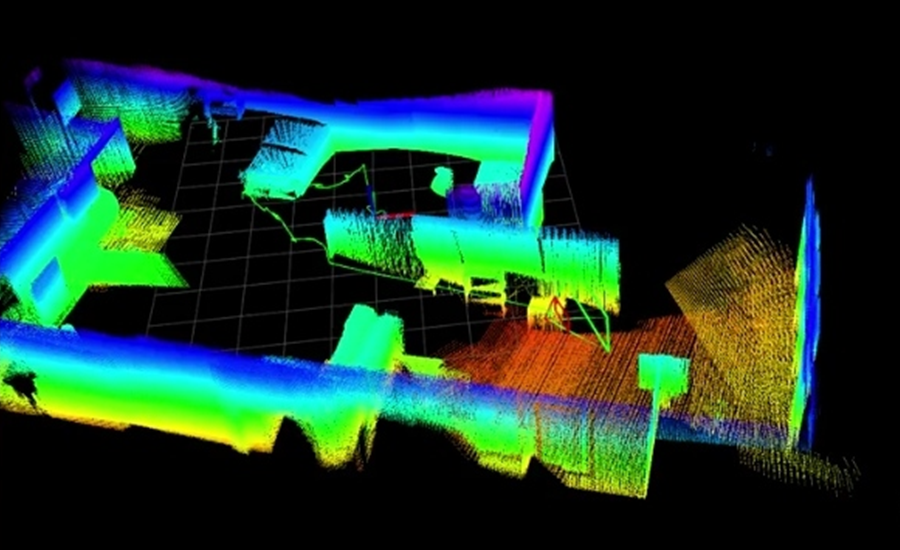
The robotic vision system of MIDRES consists of two main functionalities. Through the Simultaneous Localization and Mapping mechanism, the developed aerial vehicle is able to perceive the complex structure of the environment and move avoiding potential obstacles. This operation is not based on classic global positioning techniques and sensors, which require the installation of additional infrastructure or the ability to receive satellites signals (e.g., GNSS). Instead, it exclusively uses measurements from sensors mounted on the UAV, such as RGB and depth cameras, Laser Range Finders, and IMU.
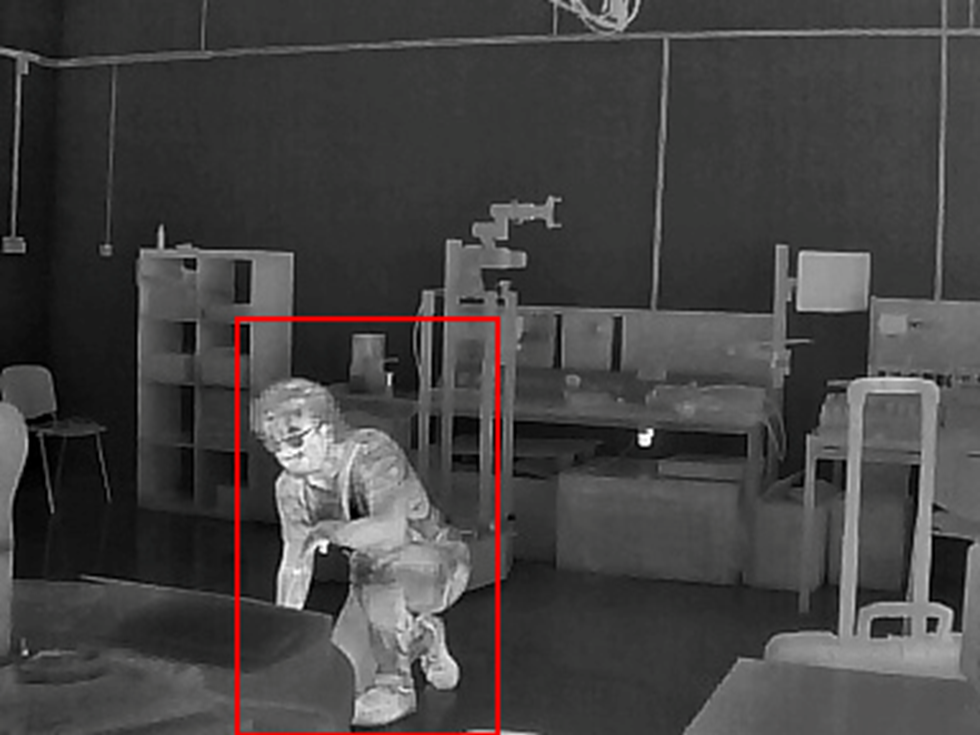
In addition, through the Human Detection mechanism, the aerial vehicle is able to identify people who may be in danger. This function is based on the measurements of the thermal camera installed to the aircraft. However, as is obvious, the human body is not the only medium that yields a strong thermal footprint, as the same can be true for specific entities located in the area to be explored, such as hot tubes, fire, and others. For this reason, the methods developed utilize deep learning technologies in order to separate objects and identify hot bodies that present a human silhouette. Thus, through an extensive set of training images, the vision system of MIDRES can detect people, even when they are partially occluded by objects and other obstacles of the environment.
Finally, the above results are transferred to the ground station and projected to the operators in a direct, comprehensive, and easily manageable manner. The user interface presents the three-dimensional mapping of the environment in real time, as it is explored, while in the case of detecting human presence, additional special signage is provided that warns the operator of its location.